Solder joints without permanent metallic connection between solder and one of the contact areas (or both).
CMC
Description:
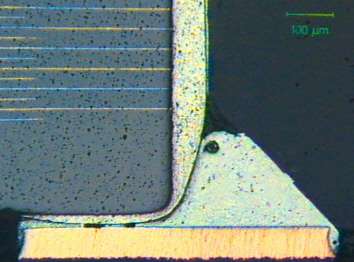
Cold solder joint at a CMC. The micrograph clearly shows the crack between the contact area of the component and the solder. This defect is difficult to detect from outside. There are a lot of reasons for this defect. The component should be replaced during rework. Observe solder parameters! (solder tip temperature
Causes/Remedy:
- long-term mechanical / thermal stress, therefore formation of crack along intermetallic zone
- poor wettability of component
- contamination of surfaces to be joined through fat or foreign substances
 Source:
Source:Microsection
SOT 23
Description:
Cold solder joint at a SOT23 component. (right). All solder joints reveal poor solder fillets. Moreover the two pads on the left show solder drain traces. In addition this component is characterized by substantial displacement. During rework this component has to be totally removed from the assembly
Observe precautions for handling ESD!
Causes/Remedy:
- poor wettability of component
- unsuitable soldering parameter: soldering temperature, soldering time
- pollution of the solder (alloy)
 Source:
Source:SEM
Passives
Description:
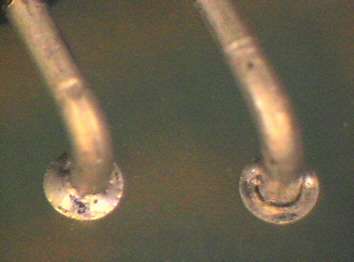
Cold solder joint at a resistor (THD, right). The defect is clearly visible at the seam between pin and solder eye. It cannot only be due to manufacturing faults but also to mechanical stress at a later date. Rework has to make sure that wetting is complete and the solder fillet well executed in the through-hole.
Causes/Remedy:
- mechanical stress
- poor solder fillet in through-hole / wetting
- contamination of surfaces to be joined
 Source:
Source:visual, optical inspection - general view
Description:
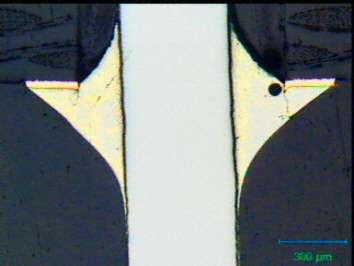
The cracks in the solder joint parallel to the lead cannot be detected from outside easily. The microsection reveals this defect. In many cases microcracks form around the hem of the solder joint which can be detected from outside.
Causes/Remedy:
- mechanical load or damage to the solder joint
- overlong leads were cut off after soldering - mechanical load
- thermal stress to solder joint through extreme temperature changes caused defect
 Source:
Source:Microsection
TO220
Description:
Cold solder joint at a TO220. This defect is due to excessive mechanical stress. There are cracks at all three solder joints. There is no contact between lead and solder. This defect is difficult to detect because it is not or only hardly visible from outside. Rework has to make sure that wetting is complete and that the solder fillet is well executed.
Causes/Remedy:
- mechanical stress
- vibration and an unsuitable geometry of the component caused the damage to the joints
- Contamination of the joining surfaces
 Source:
Source:visual, optical inspection - general view
Our analytics team can help you find the cause.
go to failure analysis at TechnoLab
