CMCs potentially pose quite a few problems as their monolithic, multilayer ceramic bodies are very susceptible to thermic and mechanical stress.
Description:
Typical crack visible from outside, due to excessive temperature gradient during the soldering process. The different temperature expansion coefficients of the component and the base material can cause mechanical stress after the soldering process and also damage to the components. Mechanical stress which the assemblies are exposed to when they are separated from the web (bending, torsion) considerably influences possible damage.
Causes/Remedy:
- insufficient component quality
- deficiencies in the process parameter (heating-up/cooling-down too fast)
- previous mechanical damage to ceramic body
 Source:
Source:visual, optical inspection - general view
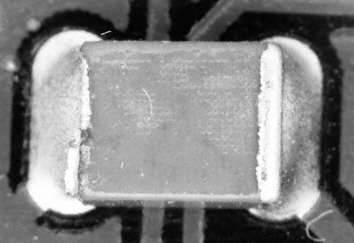
Description:
In addition to the typical cracks the photos also reveal a separation of the contact metallization. This is mainly due to manufacturing defects by the component manufacturer, but secondly also to insufficient parameter in the wave soldering process. (Separation of metallization because of excessive soldering contact time). Not acceptable.
Causes/Remedy:
- insufficient component quality
- deficiencies in the process parameter (heating-up/cooling-down too fast)
- previous mechanical damage to ceramic body
 Source:
Source:visual, optical inspection - general view
Description:
Clearly visible crack in the ceramic body of the component. Same context as above.
Causes/Remedy:
- insufficient component quality
- deficiencies in the process parameter (heating-up/cooling-down too fast)
- previous mechanical damage to ceramic body
 Source:
Source:visual, optical inspection - general view
Description:
This CMC completely broke off the assembly due to thermal stress.It cannot be excluded, however, that this component had been previously damaged mechanically. Rework absolutely necessary.
Causes/Remedy:
- insufficient component quality
- deficiencies in the process parameter (heating-up/cooling-down too fast)
- previous mechanical damage to ceramic body
 Source:
Source:SEM
Our analytics team can help you find the cause.
go to failure analysis at TechnoLab
